赫夫曼编码
1. 简介
- 赫夫曼编码也翻译为 哈夫曼编码(Huffman Coding),又称霍夫曼编码,是一种编码方式, 属于一种程序算法
- 赫夫曼编码是赫哈夫曼树在电讯通信中的经典的应用之一。
- 赫夫曼编码广泛地用于数据文件压缩。其压缩率通常在 20%~90%之间
- 赫夫曼码是可变字长编码(
VLC)的一种。Huffman 于 1952 年提出一种编码方法,称之为最佳编码。
2. 原理
通信领域中信息的处理方式–定长编码
通信领域中信息的处理方式–变长编码

3. 赫夫曼编码实现步骤
3.1 准备工作
- 构造节点类
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
|
class Node implements Comparable<Node>{
Byte data;
int weight;
Node left;
Node right;
public Node(Byte data, int weight) {
this.data = data;
this.weight = weight;
}
@Override
public int compareTo(Node o) {
return this.weight - o.weight;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Node [data=" + data + ", weight=" + weight + "]";
}
public void preOrder() {
System.out.println(this);
if(this.left != null) {
this.left.preOrder();
}
if(this.right != null) {
this.right.preOrder();
}
}
}
|
- **
private static List<Node> getNodes(byte[] bytes);**把字符数组转换成List [Node[data=97,weight=5],Node[data=xx,weight=x],…..]
private static Map<Byte, String> huffmanCodes = new HashMap<Byte,String>();private static StringBuilder stringBuilder = new StringBuilder();
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
|
private static List<Node> getNodes(byte[] bytes){
ArrayList<Node> nodes = new ArrayList<Node>();
HashMap<Byte,Integer> counts = new HashMap<>();
for(byte b: bytes) {
Integer count = counts.get(b);
if(count == null) {
counts.put(b,1);
}else {
counts.put(b,count+1);
}
}
for(Map.Entry<Byte, Integer> entry:counts.entrySet()) {
nodes.add(new Node(entry.getKey(), entry.getValue()));
}
return nodes;
}
private static Map<Byte, String> huffmanCodes = new HashMap<Byte,String>();
private static StringBuilder stringBuilder = new StringBuilder();
|
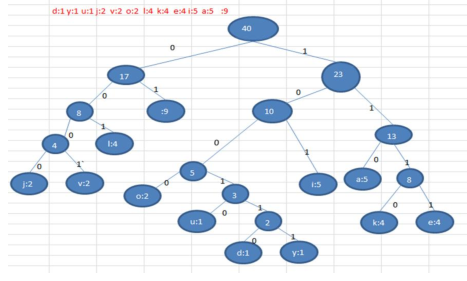
3.2 构成赫夫曼树
从小到大进行排序, 将每一个数据,每个数据都是一个节点 , 每个节点可以看成是一颗最简单的二叉树
取出根节点权值最小的两颗二叉树
组成一颗新的二叉树, 该新的二叉树的根节点的权值是前面两颗二叉树根节点权值的和
再将这颗新的二叉树,以根节点的权值大小 再次排序, 不断重复 1-2-3-4 的步骤,直到数列中,所有的数据都被处理,
就得到一颗赫夫曼树
代码实现
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
|
private static Node createHuffmanTree(List<Node> nodes) {
while(nodes.size()>1) {
Collections.sort(nodes);
Node leftNode = nodes.get(0);
Node rightNode = nodes.get(1);
Node parentNode = new Node(null, leftNode.weight+rightNode.weight);
parentNode.left = leftNode;
parentNode.right = rightNode;
nodes.remove(leftNode);
nodes.remove(rightNode);
nodes.add(parentNode);
}
return nodes.get(0);
}
|
3.3 获得赫夫曼编码
根据赫夫曼树,给各个字符,规定编码 (前缀编码), 向左的路径为 0 向右的路径为 1 , 编码如下
- o: 1000
- u: 10010
- d: 100110
- y: 100111
- i: 101
a : 110
- k: 1110
- e: 1111
- j: 0000
- v: 0001
l: 001
- : 01
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
|
private static void getCodes(Node node,String code,StringBuilder stringBuilder) {
StringBuilder stringBuilder2 = new StringBuilder(stringBuilder);
stringBuilder2.append(code);
if(node != null) {
if(node.data == null) {
getCodes(node.left,"0", stringBuilder2);
getCodes(node.right, "1", stringBuilder2);
}else {
huffmanCodes.put(node.data, stringBuilder2.toString());
}
}
}
private static Map<Byte, String> getCodes(Node root){
if(root == null) {
return null;
}
getCodes(root.left,"0",stringBuilder);
getCodes(root.right,"1",stringBuilder);
return huffmanCodes;
}
|
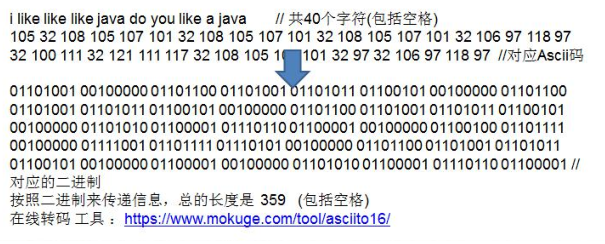
- 按照上面的赫夫曼编码,我们的”i like like like java do you like a java” 字符串对应的编码为 (注意这里我们使用的无损压缩)
1010100110111101111010011011110111101001101111011110100001100001110011001111000011001111000100100100110111101111011100100001100001110 - 通过赫夫曼编码处理 长度为 133,原来长度是 359 , 压缩了 (359-133) / 359 = 62.9%
- 此编码满足前缀编码, 即字符的编码都不能是其他字符编码的前缀。不会造成匹配的多义性赫夫曼编码是无损处理方案(NB)
注意:这个赫夫曼树根据 排序方法不同,也可能不太一样,这样对应的 赫夫曼编码也不完全一样,但是 wpl 是
一样的,都是最小的, 最后生成的赫夫曼编码的长度是一样。
3.4 完成压缩–生成赫夫曼编码
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
|
private static byte[] zip(byte[] bytes,Map<Byte,String> huffmanCodes2) {
StringBuilder stringBuilder = new StringBuilder();
for (byte b : bytes) {
stringBuilder.append(huffmanCodes2.get(b));
}
int len;
if(stringBuilder.length()%8 == 0) {
len = stringBuilder.length()/8;
}else {
len = stringBuilder.length()/8 + 1;
}
byte[] huffmanCodeBytes = new byte[len];
int index = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < stringBuilder.length(); i += 8) {
String strByte;
if(i+8 > stringBuilder.length()) {
strByte = stringBuilder.substring(i);
}else {
strByte = stringBuilder.substring(i,i+8);
}
huffmanCodeBytes[index] = (byte)Integer.parseInt(strByte,2);
index++;
}
return huffmanCodeBytes;
}
|
3.5 整合压缩方法–方便调用
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
|
public static byte[] huffmanZip(byte[] bytes) {
List<Node> nodes = getNodes(bytes);
Node huffmanRootNode = createHuffmanTree(nodes);
Map<Byte, String> huffmanCodes = getCodes(huffmanRootNode);
byte[] huffmanCodeBytes= zip(bytes, huffmanCodes);
return huffmanCodeBytes;
}
|
3.6 数据解压
- 前面我们得到了赫夫曼编码表和对应的编码 byte[] , 即:[-88, -65, -56, -65, -56, -65, -55, 77, -57, 6, -24, -14, -117, -4, -60, -90, 28]
- 现在要求使用赫夫曼编码表和编码, 进行解码,又重新得到原来的字符串”i like like like java do you like a java”
- 思路:解码过程,就是编码的一个逆向操作。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
|
private static String byteToString(boolean flag,byte b) {
int temp = b;
if(flag) {
temp |= 256;
}
String str = Integer.toBinaryString(temp);
if(flag) {
return str.substring(str.length()-8);
}else {
return str;
}
}
public static byte[] decode(Map<Byte,String> huffmanCodes,byte[] huffmanBytes) {
StringBuilder stringBuilder = new StringBuilder();
byte bs;
for (int i = 0; i < huffmanBytes.length; i++) {
bs = huffmanBytes[i];
boolean flag = (i == huffmanBytes.length -1);
stringBuilder.append(byteToString(!flag,bs));
}
Map<String,Byte> map = new HashMap<String,Byte>();
for(Map.Entry<Byte,String> entry : huffmanCodes.entrySet()) {
map.put(entry.getValue(),entry.getKey());
}
List<Byte> list = new ArrayList<Byte>();
for (int i = 0; i < stringBuilder.length();) {
int count = 1;
boolean flag = true;
Byte b = null;
String key = "";
while(flag) {
if ((i+count)>stringBuilder.length()-1) {
key =stringBuilder.substring(i);
break;
}else {
key = stringBuilder.substring(i,i+count);
}
b = map.get(key);
if(b == null) {
count++;
}else {
flag = false;
}
}
list.add(b);
i += count;
}
byte[] bytes = new byte[list.size()];
for (int i = 0; i < bytes.length-1; i++) {
bytes[i] = list.get(i);
}
return bytes;
}
|
3.7 实现文件的压缩
- 我们学习了通过赫夫曼编码对一个字符串进行编码和解码, 下面我们来完成对文件的压缩和解压
- 具体要求:给你一个图片文件,要求对其进行无损压缩, 看看压缩效果如何。
- 思路:读取文件-> 得到赫夫曼编码表 -> 完成压缩
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
|
public static void zipFile(String srcFile,String destFile) {
OutputStream os = null;
ObjectOutputStream oos = null;
FileInputStream fis = null;
try {
fis = new FileInputStream(srcFile);
byte[] b = new byte[fis.available()];
fis.read(b);
byte[] huffmanBytes = huffmanZip(b);
os = new FileOutputStream(destFile);
oos = new ObjectOutputStream(os);
oos.writeObject(huffmanBytes);
oos.writeObject(huffmanCodes);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
System.out.println(e.getMessage());
}finally {
try {
fis.close();
oos.close();
os.close();
} catch (Exception e2) {
e2.getStackTrace();
}
}
}
|
3.8 实现文件解压
- 具体要求:将前面压缩的文件,重新恢复成原来的文件。
- 思路:读取压缩文件(数据和赫夫曼编码表)-> 完成解压(文件恢复)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
|
public static void unZipFile(String zipFile,String destFile) {
InputStream is = null;
ObjectInputStream ois = null;
OutputStream os = null;
try {
is = new FileInputStream(zipFile);
ois = new ObjectInputStream(is);
byte[] huffmanBytes = (byte[])ois.readObject();
Map<Byte,String> huffmanCodes = (Map<Byte,String>)ois.readObject();
byte[] bytes = decode(huffmanCodes,huffmanBytes);
os = new FileOutputStream(destFile);
os.write(bytes);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
try {
os.close();
ois.close();
is.close();
} catch (Exception e2) {
e2.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
|
3.8 测试结果
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
|
public class HuffmanCode {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String zipFile = "E:/file/testRes.zip";
String destFile = "E:/file/test3.jpg";
unZipFile(zipFile,destFile);
System.out.println("解压成功");
}
}
|







